Google began a project in 2021 called “Core Web vitals” to improve the page experience for users. You probably already know that anytime we need information from the internet, we typically resort to Google Search, which is precisely what Google wants us to do.
If Google is indexing your website on the web and a user is searching for some information on Google, Google wants that user to have the best experience on their website, which is indexed on their platform.
To measure this, Google has introduced “core web vital” based on the following four things: performance, accessibility, best practices, and SEO.
The Google Page Experience includes “Core Web Vitals” as one of its subsets. Core Web Vitals are a group of high-level metrics that Google made to describe what it’s like to use the web.
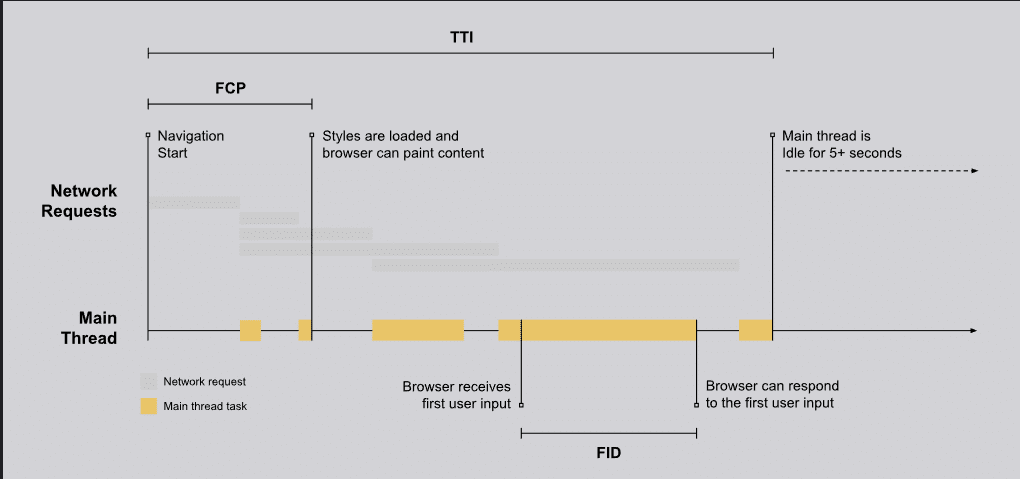
Google thinks these vitals are very important because they show how happy or unhappy a user is with a website. The Largest Contentful Paint, the First Input Delay, and the Cumulative Layout Shift are the three core Web Vitals metrics that are measured.
To put it another way, Core Web Vitals are utilised to evaluate how users interact with a particular website.
What is Core Web Vital
Google refers to the overall ovulation of “Page Experience” as “Core Web Vitals.” “Page experience” is an umbrella term.
3 Pillars of Core Web Vitals
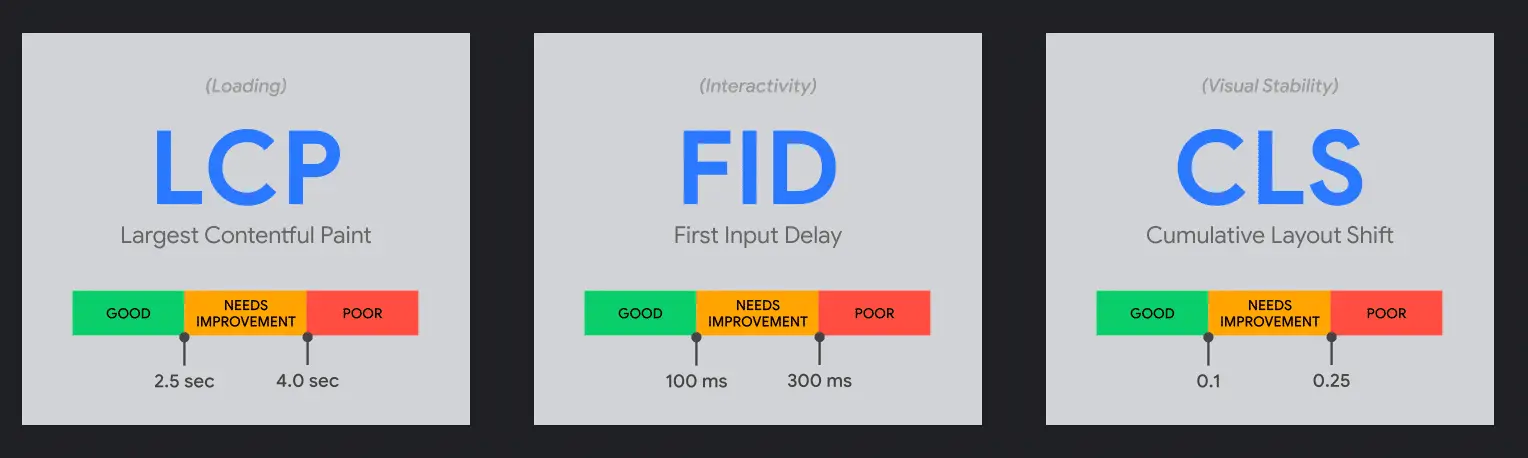
The metric Cumulative Layout Shift, or “CLS,” considers Visual Stability, Loading for the Largest Contentful Paint, and Interactivity for “First Input Delay.”
The First Input Delay is going to be replaced by “Interaction to Next Paint (INP)” in 2024 as announced by Google here.
Even though there have been other user experience ranking signals in the past, such as mobile friendliness, HTTPS security, and intrusive interstitials, the Core Web Vitals are different because they are advanced and emulate how users use search engines.
Because of this, they can tell you with 99.9% accuracy how users interact with your website.
For both mobile and desktop, each of the vitals evaluates the performance of a different aspect of your website and gives you a grade of either “good,” which indicates that it could use some improvement, or “poor.”
In the enhancements section of your Google Search Console account, you can find the data that makes up the most important parts of your website.
How to Audit your Site for Core Web Vital
Several tools are available to assist you in analyzing the fundamental components of your website, which you can do if you so desire.
Google’s Pagespeed insights is one of them which you can check here.
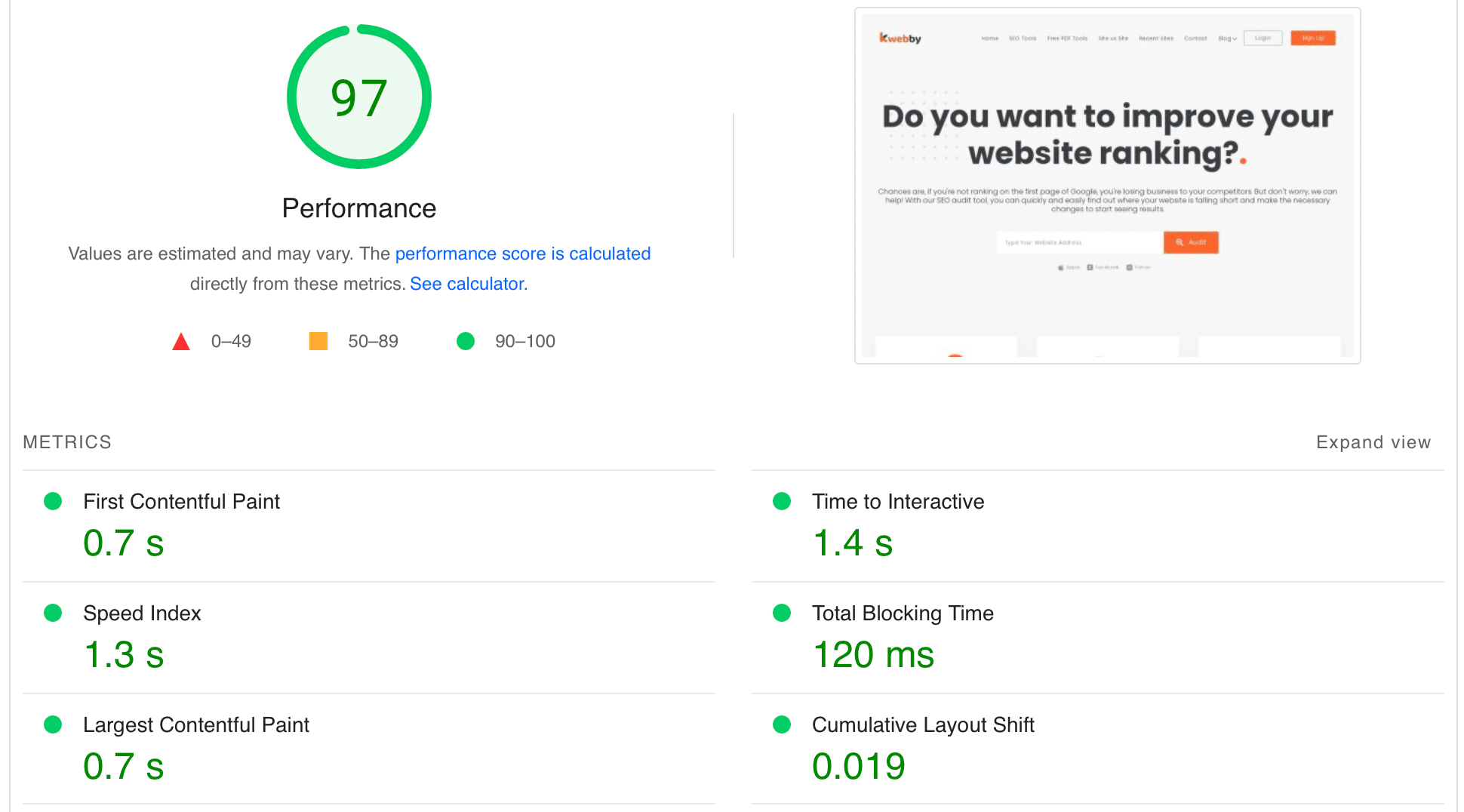
Just type your URL and click on “Analyze”.
Good Scores for LCP, CLS, and FID measures
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
The load time for the material that takes the longest to load on a webpage, such as photos, videos, or text, is measured by the LCP. Put another way, the amount of time required to view the page’s graphical components.
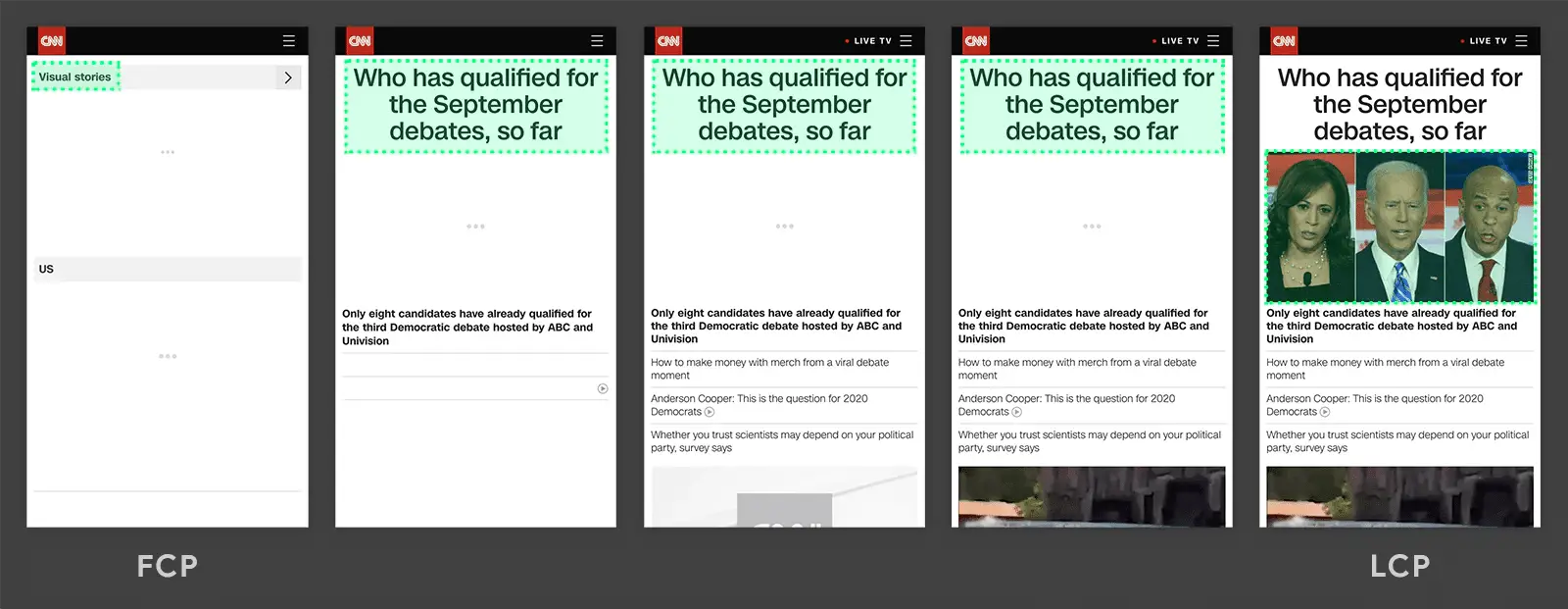
Have you ever visited a website and couldn’t view any visual elements and all you could see was a blank screen?

Or has the website you were using to search for something crashed while you were using it?
Because the LCP measures your page based on how quickly it provides users with something to watch, it is in your best interest for things to appear on the site as soon as possible.
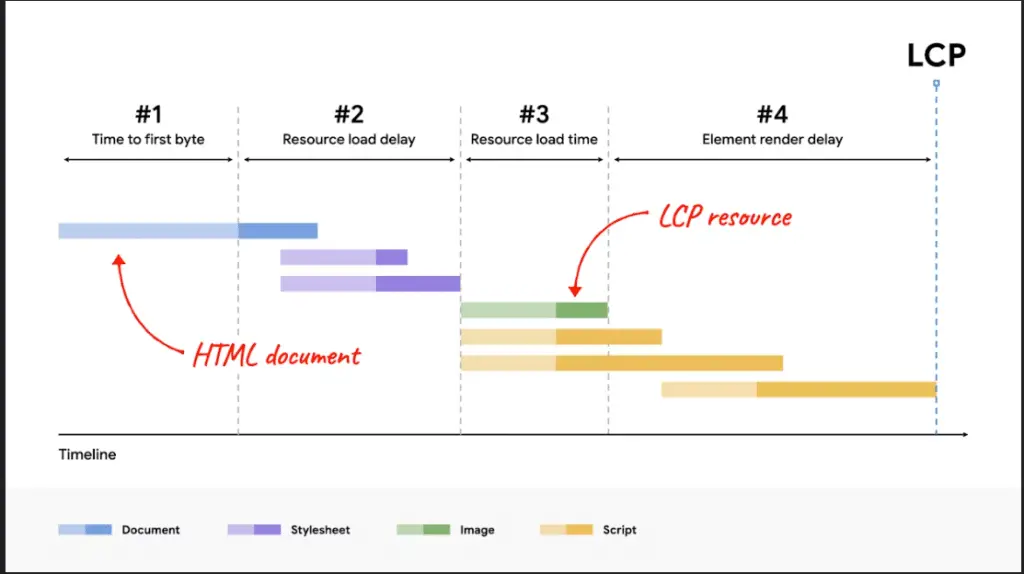
According to Google, a decent score requires a loading time of 2.5 seconds or less, at the very least. You can use Google PageSpeed Insights to check how well you scored on the LCP.

Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS evaluates the consistency of your page while it is loading. Have you ever been on a website and noticed that the layout moves and, as a result, you clicked on the wrong option? If this is the case, what you have witnessed is referred to as “page instability.”
To put it another way, this is the process through which the components of your website change position while the page loads.
This will make the CLS score high, which is seen as a bad thing. Users will become frustrated when elements on a site start moving unexpectedly. This factor is included in the scale used to rank the user experience. You will have achieved a satisfactory score if your CLS score is 0.1 or lower.
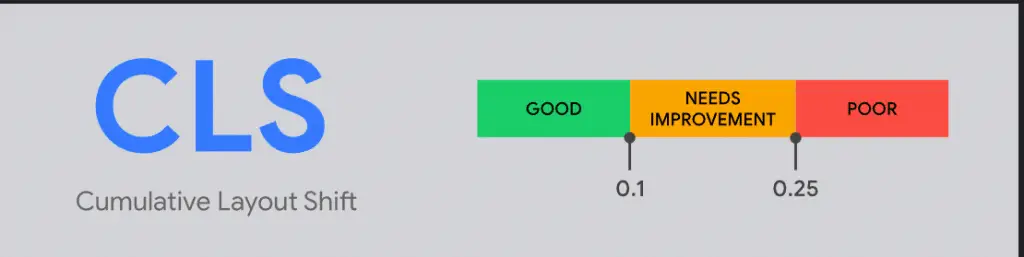
If you want a decent score on the CLS, it is important that the parts of your page remain somewhat consistent while the page is loading.
When this is done, visitors won’t have to relearn the locations of links, images, and forms when the page is fully loaded, eliminating the possibility that they will select the erroneous option by accident.
First Input Delay (FID)
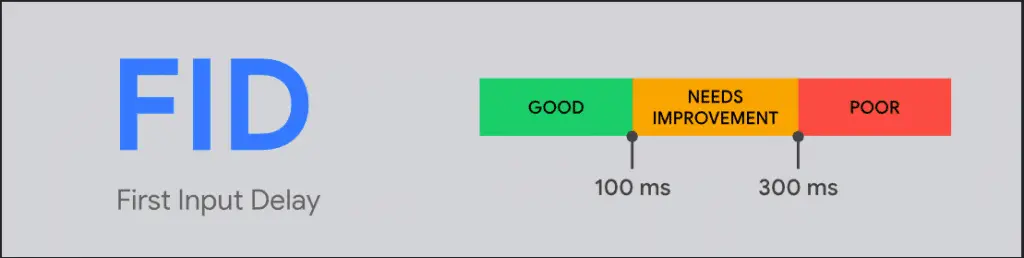
The next component, the FID, indicates how quickly your website reacts to the actions taken by users while they are on the page. The difference lies in whether or not your website reacts to the actions that are taken by your users.

Google gives FID a lot of weight because it takes into account how real people interact with your websites and other online properties. Scrolling, clicking, or pressing keys are all examples of interaction.
The following are some examples, but the list is not exhaustive:
Simply going to a specific link on the website
Putting one’s email address into a designated space
picking something from the menu to do
On a mobile device, the popup text can be opened.
Moving down the page when browsing the website
Google says that a page that responds slowly to user actions makes for a bad user experience. They say that the best FID score is less than 100 milliseconds.
Core Web Vital’s Impact on SEO
Core Web Vitals help web developers ensure that website visitors have a good time. SEO is essential for websites as it shows how users experience your site.
Core Web Vitals are the ranking signals as part of one of the Page Experience signals mentioned by google’s official blog here.

Because of this, customers are happier with their experience, more likely to come back to your website, and more likely to tell others about it. On the other hand, people are less likely to return to a website if the pages load slowly, are unstable, or are packed with popups.
Now consider how this affects Google’s brand and the company’s revenue. If you keep clicking on links in the search engine results page (SERP) that take you to unsatisfactory pages, you will become frustrated with Google.
You might switch to a different search engine in the future, meaning that Google would make less money from ads.
The Google Core Web Vitals are a set of measurable SEO performance metrics that give you an idea of how people interact with your website.
They give you precise data points that can be measured, which can help you improve the entire user experience on your website. Users are more inclined to return to a site if they have had a positive experience.
It is also important to know that, despite the importance of Core Web Vitals, Google will still try to rank pages based on the overall quality of the information they provide, even if the page’s user experience is poor.
Ways to Improve Core Web Vitals report
How can you optimise your WordPress site to increase your Core Web Vitals scores if you are not fulfilling Google’s recommendations for the three metrics that make up Core Web Vitals?
Tools you need for WordPress is WPRocket.
Each measure requires a unique set of techniques to be implemented. Most optimizations involve using WordPress’ best practices for performance, but some areas are more critical than others.
This is why choosing the best WordPress caching plugin will help you without you having to do any work.
How to improve Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Optimising for the Largest Contentful Paint is the easiest measure to understand because it is almost entirely comprised of the performance best practices for WordPress:
Remove unwanted scripts from third-party websites
Scripts from third-party websites drastically slow down the loading speed of your page. Every third-party script you add to your website adds 34 milliseconds to the time it takes to load.
for WordPress websites, you should download, Install and activate WP-Rocket Plugin; afterwards go to settings > wp rocket option as below;
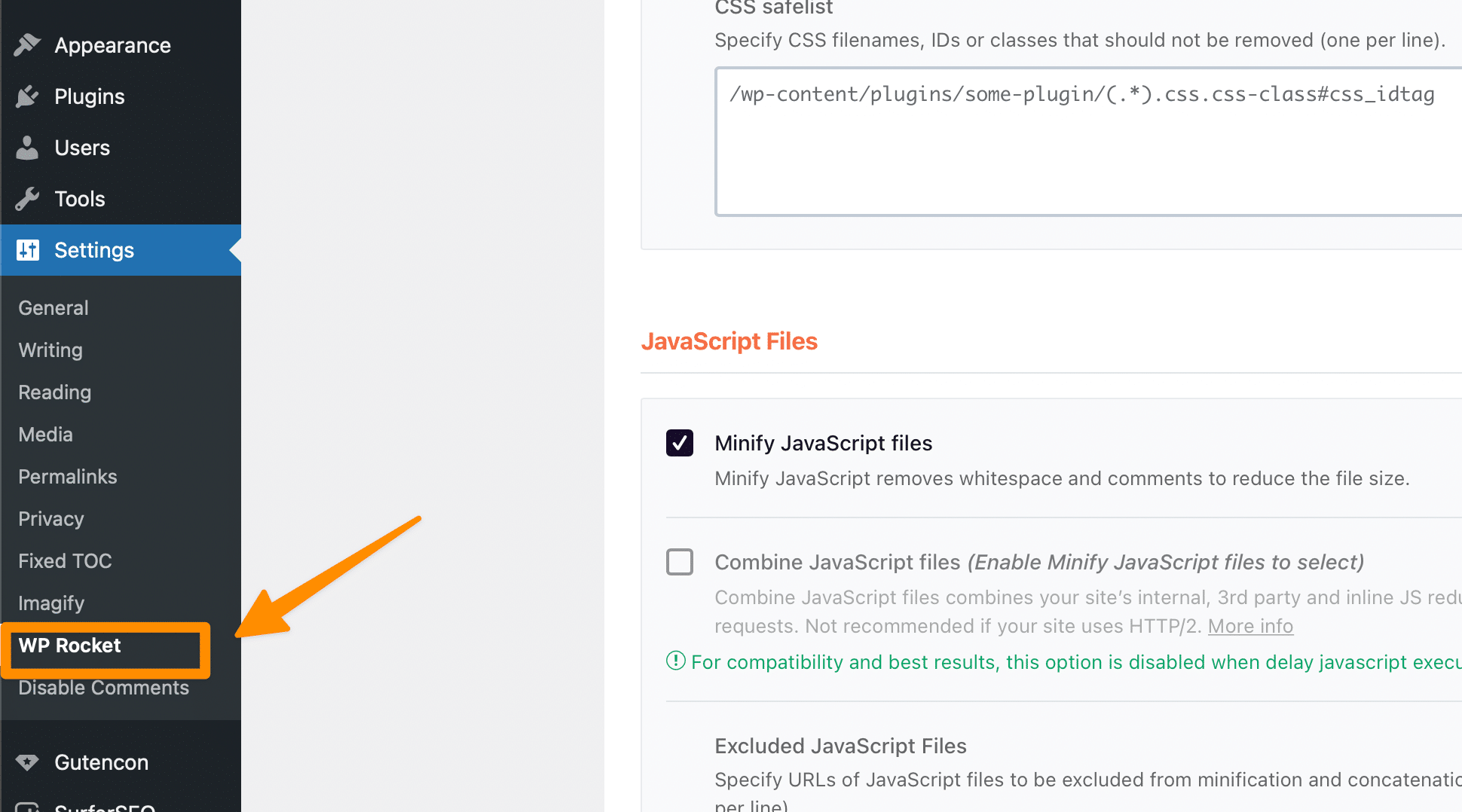
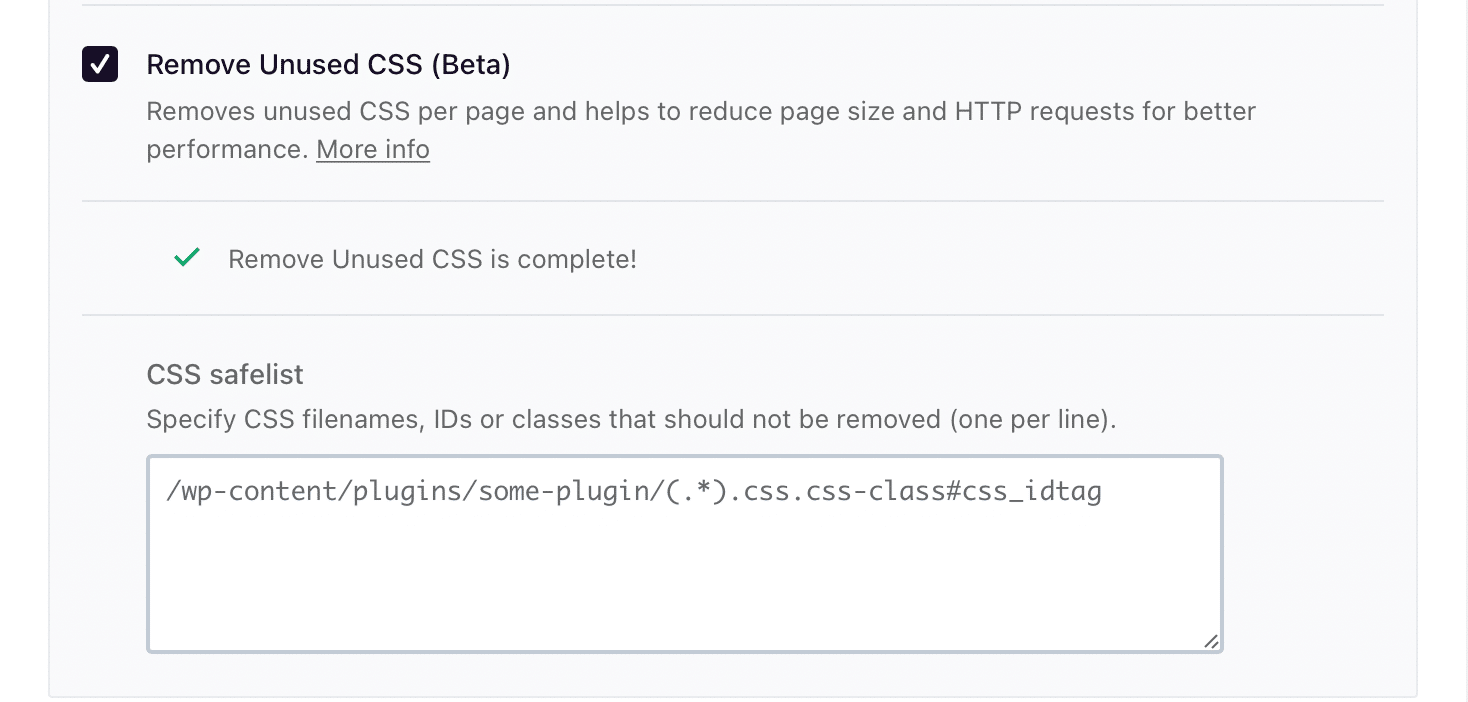
Now navigate to File optimization on the left and check the following option of remove unused CSS for CSS files;
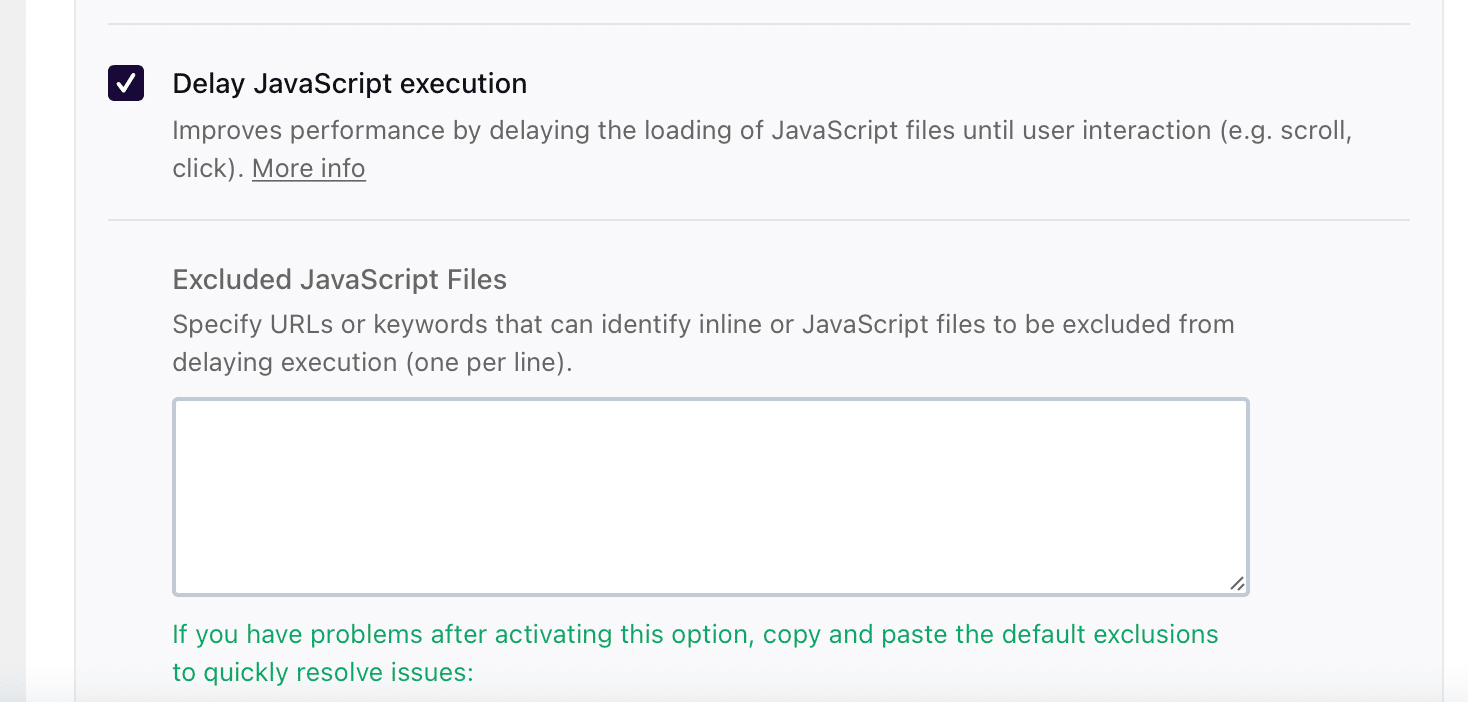
If you use various scripts like analytics, social plugins etc then you can delay javascript execution by enable in the same dashboard as below;
Compress your cascading style sheets (CSS) and Javascript (JS) Files
Having a huge amount of CSS can considerably slow down the LCP process. You can minify CSS or JS files using our tools i.e. CSS minifier and JS minifier.
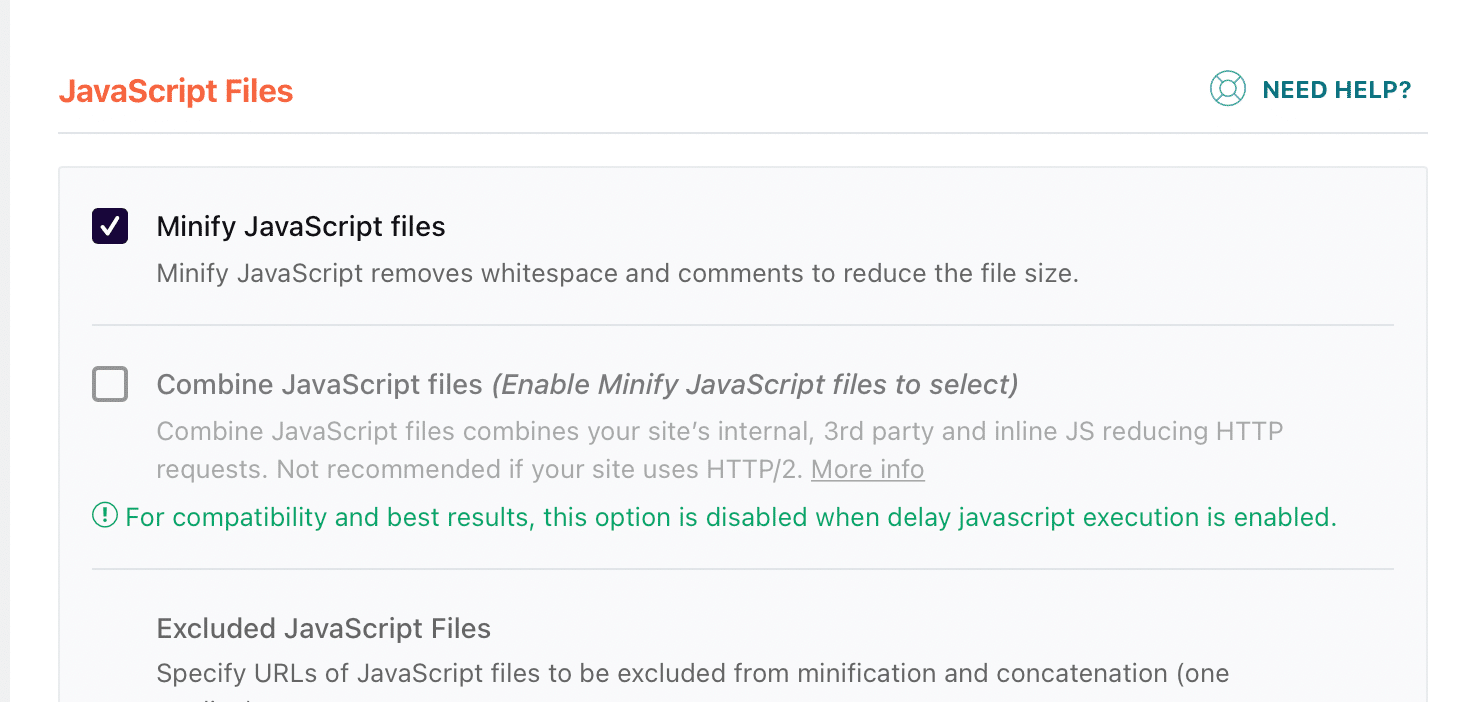
For WordPress you can use WProcket plugin to minify the same by going into settings > wp rocket > File optimization. And then, first, you need to check the “Minify CSS Files” option below;

For JS, scroll down to the option of “Minify JS Files” as below;
Consider upgrading your website host
The quality of your website host directly impacts how quickly your site loads.
Enable lazy loading
This will prevent images from loading on the website until the user scrolls down the page. Lazy loading is a feature found in many content management systems. This makes it much easier for you to reach LCP in a shorter time.
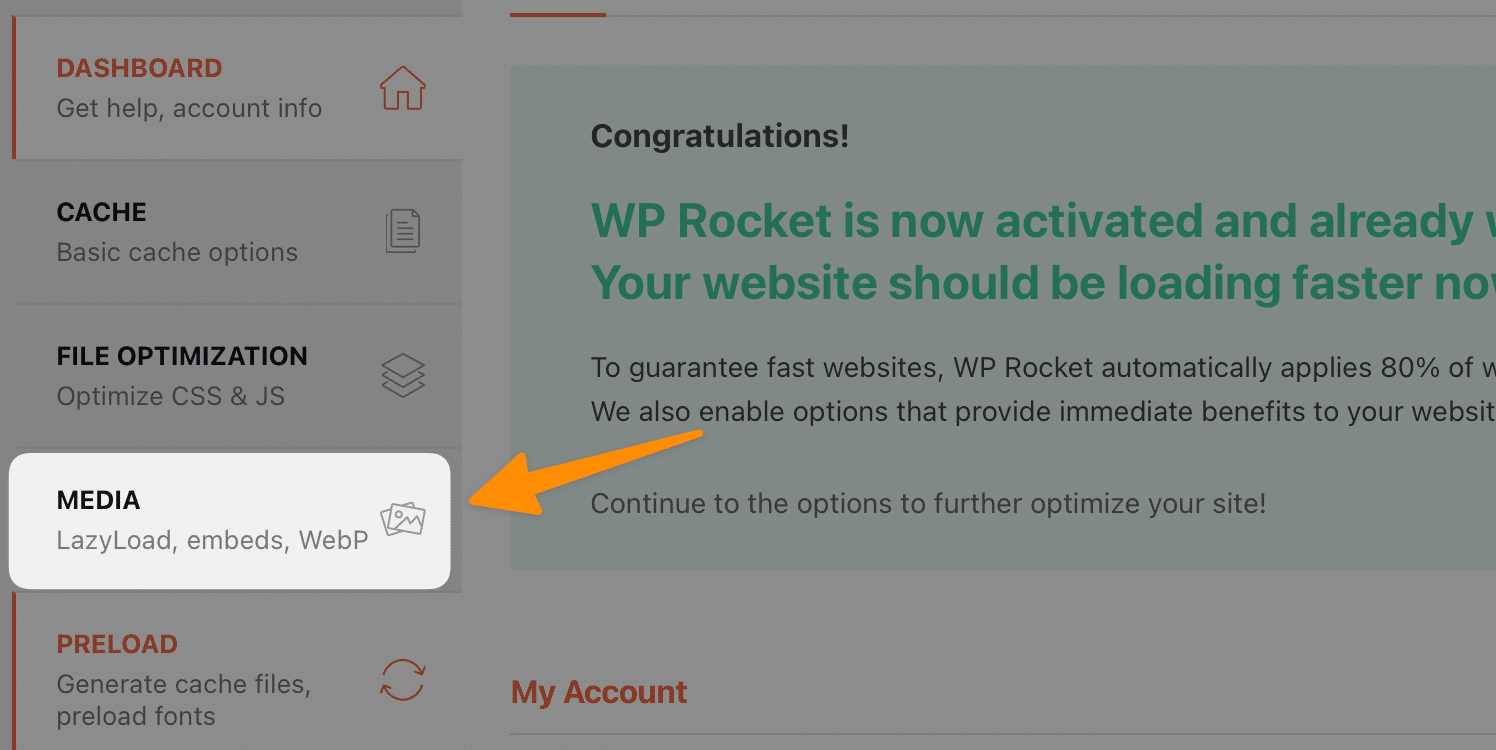
For WordPress users, You need one plugin, i.e. WP Rocket; after activating the same, go to settings > wp rocket > Media;
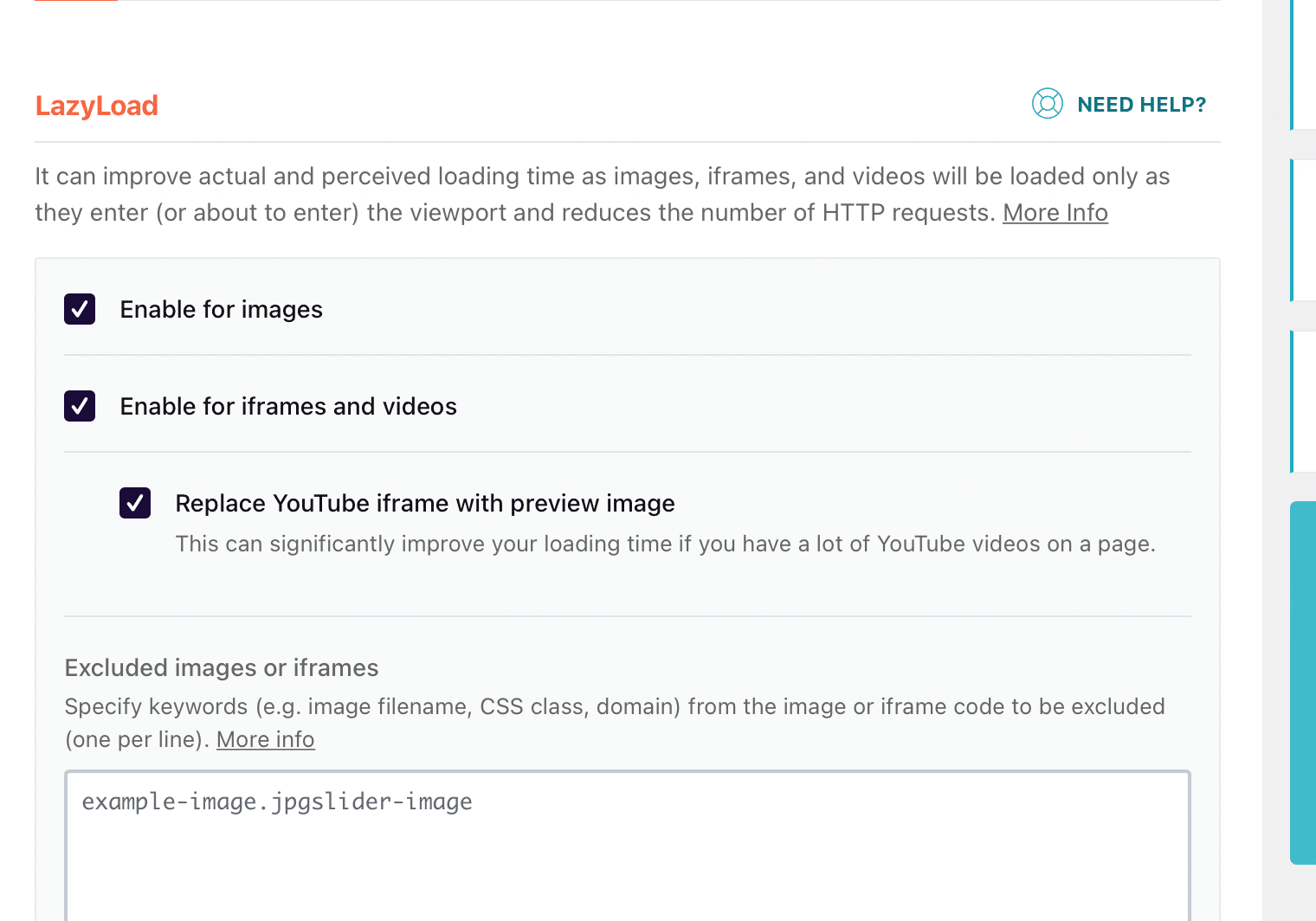
And then select the “Lazyload” options as below;
And as for non-WordPress users, we have described the process in the video below;
Get rid of huge site elements
Google Page Speed Insight can inform you if your website contains an element that slows down your LCP. This provides you with the opportunity to either optimise or get rid of the piece in question.
How to Improve Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
A Focus on Cumulative Layout Optimisation Because it interacts more directly with the coding of your website, Shift is a slightly more complex option.
Some of the most typical issues, as well as their solutions, are as follows:
Correct Images that are missing their sizes
if you upload images through the editor in WordPress, the software will automatically add the appropriate dimensions for you. Still, if you manually add photos using your code, you must include the size. After that, you will discuss the best practice for serving of scaled photos.
Repair advertising embeds and iframes that do not have sizes.
In the same way that loading images without dimensions can cause issues, loading embeds without dimensions can also cause issues. When using these embeds, you must ensure that the sizes are always specified.
Alternatively, if you place advertisements, you should “reserve” space for each advertisement.
Optimise online fonts (FOIT/FOUT)
If you’re using custom web fonts, a Flash of Invisible Text (FOIT) or Flash of Unstyled Text (FOUT) could occur if the font loads too slowly (FOUT). Because of this, you won’t be following the PageSpeed rule that says, “Make sure text is still visible while webfont loads.”
Web font preloading is one potential solution to this problem. Keep in mind that WP Rocket will automatically optimise Google Fonts if you require assistance in this matter.
As for other fonts, the plugin assists you in resolving the issue using the Minify or Combine CSS option, which was previously described for the enhancement of LCP.
Be careful when working with injected content.
Don’t add new content on top of old content unless it’s in response to something a user did.
How to Improve First Input Delay
First Input Optimization Delay is the most difficult because it fully involves programming. The following are some of the most common problems and their solutions:
Slow down (or postpone) the execution of JavaScript
When a person tries to connect with a web page while the browser is loading JavaScript, it is tough. So, to get the best FID score, you must reduce the amount of JS on your page or delay its execution.
Get rid of any non-essential scripts that were provided by a third-party
Similar to FCP, third-party manuscripts (like Google Analytics, ads, heatmap devices, and so on) could hurt your website’s FID rating.
Make use of the cache of your internet browser.
This method makes it possible to speed up the loading of a large amount of content on your page, making the JS-filling jobs in your users’ browsers run even more quickly.
How to Fix ‘Does not use passive listeners to Improve scrolling performance’
Core web Vitals in Search Console
Google gathers Core Web Vitals as part of the Chrome User Experience Report, and the company then uses these metrics as a ranking indicator.
Click on the Core Web Vitals tab in the sidebar to learn more about how your website’s visitors use it.
After that, Google will tell you what percentage of your URLs it considers to be “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor.” The report breaks down the encounters into mobile and desktop categories.
Click the “Open Report” button to see more information about the Core Web Vitals on your site.
The bar chart shows how many of your pages already meet the standards set by Web Vitals and how many still need to be fixed.
To view all of the information, you must first click on the headers labelled “Need improvement” To see all of the information, you must first click on the “Needs improvement” and “Good” headers. By default, only “Poor” experiences are shown. and “Good,” as the default setting only displays “Poor” experiences.
Under the chart, there is a section called “Why URLs are not considered good.” This part explains which of the following three Core Web Vitals your website is not doing well on:
LCP issue: Largest Contentful Paint is too high
CLS issue: Cumulative Layout Shift is too high
FID issue: First Input Delay is too highYou can also view, beside each problem, the total number of URLs whose ranks are being affected.
Conclusion
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that let you keep an eye on how people use your website so you can keep your ranking high. To put it another way, it provides a quantitative analysis of the user experience provided by your website.
Because of this, the quality of the experiences your users have with your website will directly improve its overall performance, as well as its trustworthiness and dependability.
User pleasure is the most important factor, so you should make every attempt to improve your Core Web Vitals.