When you run a website, 404s are going to happen. They happen when a user tries to access a page that no longer exists.
A common question website owners ask:
Do 404s affect SEO rankings?
According to a Google Search Console video on a question Maria asked, 404s don’t directly hurt your site’s overall rankings; it’s how you handle them that matters.

For example, if a product has been replaced by a new one, a redirect is fine. But redirecting to unrelated or similar products is bad for user experience and can hurt your site’s credibility.
This document will cover how to handle 404s, soft 404s and custom 404 pages so your site remains valuable to users and search engines.
By understanding broken links, error messages and HTTP status codes, website owners can keep their SEO and user engagement.
Google Answers: How to handle 404s? Will You lose my rankings?
When talking about 404s, we need to answer the common question website owners ask: “I have a lot of 404s on my site. If I don’t redirect them will I lose my site’s rankings?“
According to Maria from a Google Search Console video, 404s are common but they don’t hurt your site’s overall rankings.
Google recommends:
- Acknowledge Your 404s: 404s are part of having a healthy website. They mean missing pages or links that are no longer relevant.
- Redirect Only When Necessary: If a product or page has a real replacement (like a new model of a cup), then a redirect is fine. But don’t redirect to similar or unrelated pages, it will frustrate users looking for specific information.
As Mueller;
“Redirects can play a role in dealing with old pages, but not always. For example, if you have a genuine replacement product, such as a new cup that functionally replaces a cup which is no longer produced, then redirecting is fine. On the other hand, if you just have similar pages, then don’t redirect. If the user clicked on your site in search of a knife, they would be frustrated to see only spoons. It’s a terrible user experience and doesn’t help in search.”
- Return HTTP 404 Status Codes: When an old page no longer exists and has no replacement, return a proper HTTP 404 status code. This tells search engines and users the page is truly not found.
- Create a Custom 404 Page: Create a user friendly and informative 404 error page. Use this opportunity to engage users; for example you can explain the benefits of similar items, like how spoons are better than knives to keep users interested.
As Mueller said;
“Instead, return an HTTP 404 result code. Make a great 404 page, maybe even make a 404 page that explains why spoons are superior to knives, if you can make that argument.”
- Don’t Blindly Redirect: Don’t redirect users to category pages, home pages or any unrelated content as this will hurt user experience and your site’s credibility.
As Mueller said;
“Just don’t blindly redirect to a similar page, a category page, or your home page. If you’re unsure, then don’t redirect. Accept that 404s are fine. They’re a normal part of a healthy website. “
In summary, managing 404s is important but not all 404s hurt your SEO rankings.
Accepting 404s as part of website maintenance will guide you in making decisions on redirects and user experience.
Through managing broken links, error messages and HTTP status codes website owners can maintain SEO while improving user engagement on their site.
More From the Podcast;
Also, read Google’s FAQs on 404s: Do 404 errors hurt my site?
When to Redirect 404s?
Knowing when to redirect a 404 page is key to both user experience and SEO rankings. Redirecting should be thoughtful and context based. Here are some scenarios:
Real Replacement
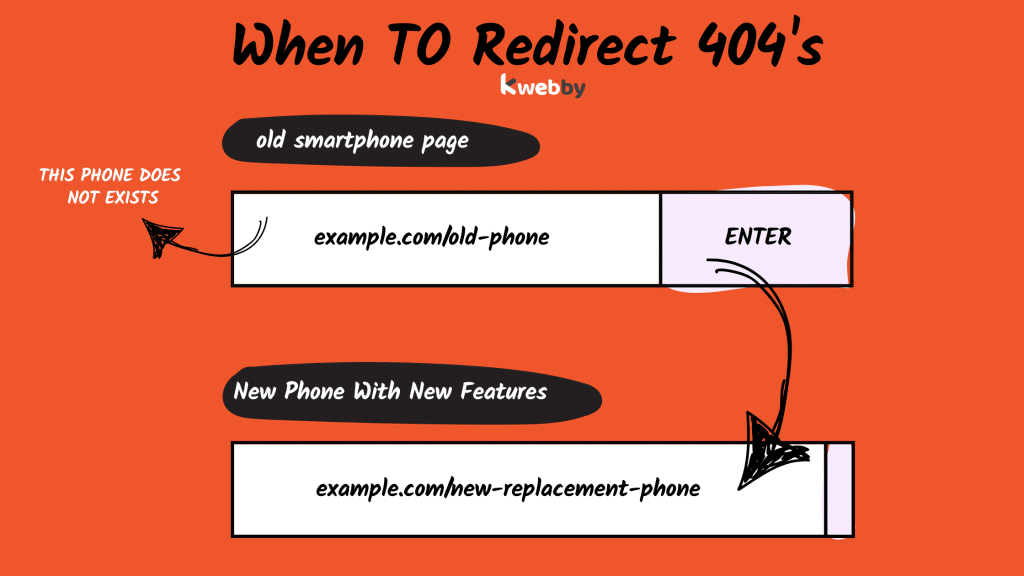
Redirecting is fine when a product or page has a real replacement.
For example if an online store replaced an older model of a smartphone with a new one, redirecting users from the discontinued model to the new one is good.
This is a direct approach so users will find what they are looking for without extra detours.
No Replacement
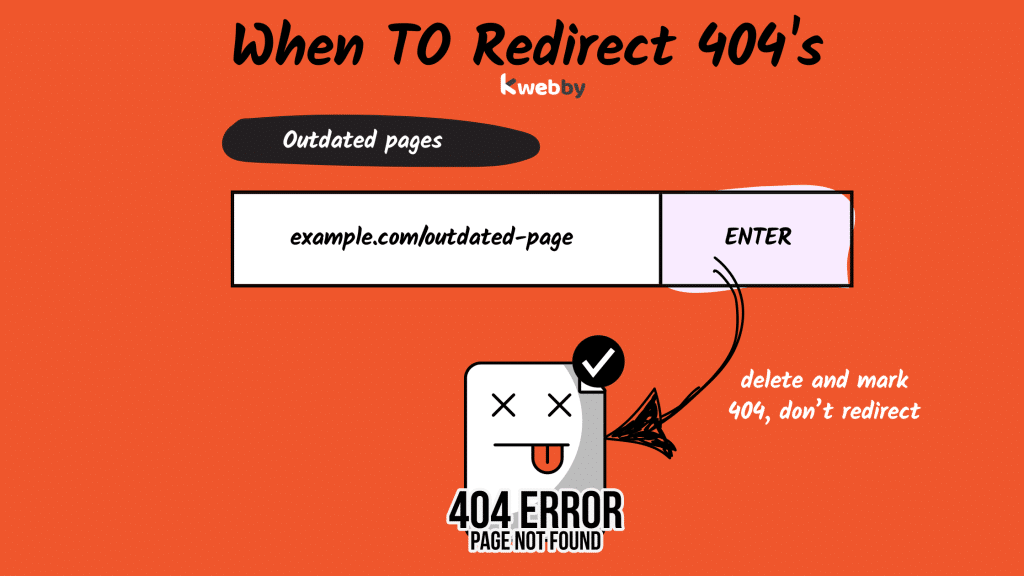
If there’s no relevant content for the missing content then don’t redirect.
For example if a blog post was removed because the information is outdated and there’s no similar post to guide users then it’s best to return a proper 404 status code.
This will tell both users and search engines the page is no longer available and will prevent unnecessary crawling of non-existent pages.
Misleading Redirects
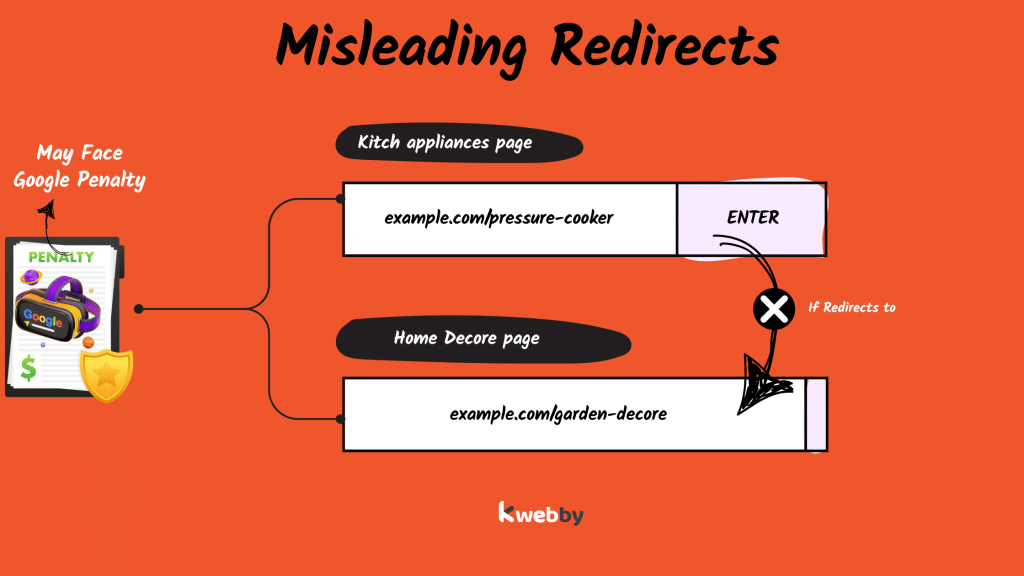
Redirecting to unrelated pages will hurt user experience and erode your site’s credibility.
For example if a user searching for a specific kitchen appliance lands on a redirected page for totally different home decor items, their frustration will lead to higher bounce rates. Blind redirects not only hurts user satisfaction but also SEO rankings.
By knowing these scenarios website owners can make decisions on when to redirect 404s and improve user engagement while keeping their site’s SEO intact. Also use tools like Google Search Central, Screaming Frog SEO Spider or broken link checkers to monitor for 404s and fix them proactively.
How to Optimize 404 Error Page for User Engagement
An optimized 404 error page is a powerful tool to maintain user engagement and overall website SEO.
By turning error pages into opportunities to guide visitors website owners can improve user experience and reduce bounce rates. Here are the steps to optimize your 404 error page for better engagement:
- Create a Clear Message: Clearly tell the user the page they are looking for is not found. Use simple language and display a plain error code (404 error code) to inform users they have hit a missing page.
- Add Navigation Links: Provide links to popular pages, categories or your main navigation menu. This gives users an alternative path to continue on your site in case they land on a broken page.
- Add a Search Bar: Add a search functionality so users can find the content they are looking for, directly address the missing page issue. The search box should be prominent to encourage interaction.
- Suggest Related Content: Proactively recommend articles or products that are related to what the user was looking for. This ties into content marketing strategy by suggesting related topics that might interest the user.
- Design a Nice Layout: A custom 404 page can capture attention and reduce frustration. Use engaging graphics and a friendly tone to humanize the error experience so users feel welcome not deterred.
- Monitor Performance: Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor your 404 pages. Analyze the data to see which links are generating soft 404s or crawl errors so you can improve based on user behavior.
- Implement HTTP Status Codes Correctly: Make sure your server returns the correct HTTP status code for 404 errors. Misconfigured status codes will lead to misleading error pages and hurt search engine rankings.
By following these steps you can turn your 404 error page into a powerful asset that keeps visitors and helps your website’s SEO. As the search engine landscape changes every website owner’s top priority is to have high quality user experience on their website.
That’s it!
In summary managing 404s is a multi faceted approach that preserves user experience and SEO rankings. By knowing when to redirect, optimizing 404 error pages and using Google Search Central and Screaming Frog to find and fix broken links website owners can minimize the impact of missing pages.
Custom 404 pages that engage visitors can turn frustration into opportunities for more interaction and improve overall engagement metrics. By monitoring your website through Google Analytics you can address soft 404s and crawl errors before they impact your search engine visibility.
As the online world changes best practices in technical SEO and content marketing and using SEO services will keep your site resilient to 404s and improve your search engine presence. Remember a well managed website with optimized error pages is a key asset to your online brand.





