Google Search Console can show a confusing status: “Page indexed without content”. This status means Google added the URL to its index, but Google did not keep meaningful page content for it. You need to confirm what Google actually fetched, find the cause, and then fix the page so Google can render and store the content.
Key Takeaways
- Use the Page indexing report to find affected URLs and patterns (templates, sections, parameters).
- Use URL Inspection to compare what you see vs what Google sees (HTML, rendered page, resources).
- Common causes include soft 404 pages, blocked resources, thin or empty templates, JS rendering issues, and wrong canonicals.
- Fixes include improving server responses, removing empty states, allowing critical resources, correcting canonicals, and strengthening internal links.
- After changes, use Validate Fix and Request Indexing to speed up reprocessing.
- To check if something is indexed, use URL Inspection, the site: operator, and page-level signals like cached content and canonical selection.
What “Page Indexed Without Content” Means in Google Search Console
This status appears when Google indexes a URL but does not store useful content for it. Google may have fetched the page, but the page returned little or no main content, or Google could not render the content. In many cases, the page looks fine to users but looks empty to Googlebot.
Before you fix anything, you need to confirm the scope and confirm what Google sees. Then you can apply a focused fix.
Why this status matters
- Google can waste crawl budget on low-value URLs.
- Your important pages can lose rankings because Google cannot use the content.
- Index bloat can grow if many empty or duplicate URLs get indexed.
Google’s Search Head John Mueller reveal why you see Page Indexed Without Content error on reddit;
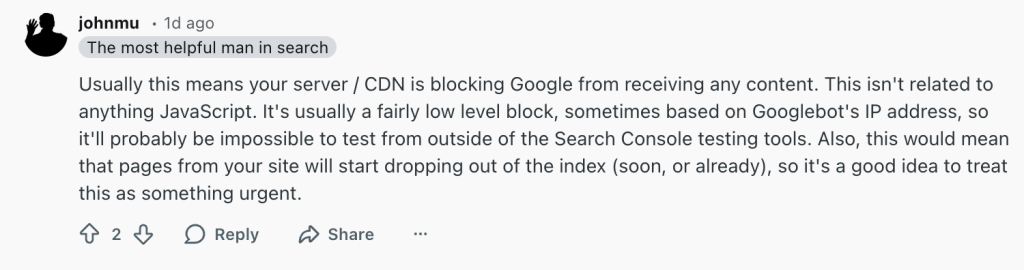
Usually this means your server / CDN is blocking Google from receiving any content. This isn’t related to anything JavaScript. It’s usually a fairly low level block, sometimes based on Googlebot’s IP address, so it’ll probably be impossible to test from outside of the Search Console testing tools. Also, this would mean that pages from your site will start dropping out of the index (soon, or already), so it’s a good idea to treat this as something urgent.
Next, you will diagnose the issue in Search Console step-by-step.
Step-by-Step: Diagnose “Page Indexed Without Content” in Search Console
Use these steps in order. Each step gives you a clear signal. Each signal points to a specific fix.
Step 1: Find the affected URLs in the Page indexing report
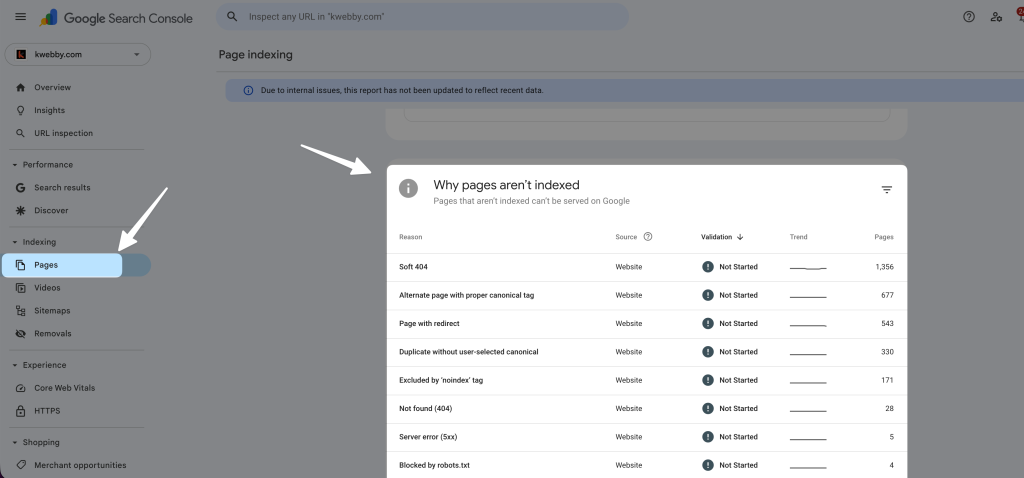
- Open Google Search Console.
- Go to Indexing → Pages (or Page indexing, based on your UI).
- Find the row for “Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt”, “Crawled – currently not indexed”, and “Page indexed without content”. These often relate.
- Click “Page indexed without content”.
- Click View data about indexed pages and export the URL list.
Now group the URLs by pattern. This step saves time.
- Group by directory:
/blog/,/category/,/products/. - Group by template type: tag pages, search pages, faceted filters.
- Group by parameters:
?sort=,?page=, tracking parameters.
Step 2: Inspect a sample URL (URL Inspection)
- Pick 3 to 5 URLs from each group.
- Use URL Inspection at the top of Search Console.
- Check Indexing status and Coverage details.
- Check Google-selected canonical vs User-declared canonical.
Then click View crawled page (or similar option) and review these items:
- HTML: Does the HTML include the main content or only placeholders?
- Screenshot: Does Google render the content or show a blank layout?
- More info → Page resources: Are CSS/JS resources blocked or failing?
Step 3: Run a live test to compare “live” vs “crawled”
- In URL Inspection, click Test Live URL.
- Compare the live rendered view to the crawled view.
If live works but crawled fails, you likely have one of these issues:
- Server blocks Googlebot sometimes (WAF, bot protection, rate limits).
- Slow responses or timeouts during crawl.
- Content loads only after user interaction.
- Rendering depends on blocked scripts or blocked APIs.
Step 4: Check server response and status codes
- Check the URL with a header tool or your server logs.
- Confirm the page returns 200 for real content pages.
- Check for 204, 206, 3xx loops, and inconsistent responses.
Many “indexed without content” cases come from pages that return 200 but show “no results” or a near-empty template. Google can treat that as a low-value page.
Step 5: Check robots.txt and blocked resources
- In Search Console, open the robots.txt report if available for your property.
- Confirm the URL is not blocked.
- Confirm critical resources are not blocked:
/js/,/css/, API endpoints used for content.
Even if the page itself is allowed, blocked CSS/JS can stop rendering. That can leave Google with empty content.
Step 6: Check canonical tags, redirects, and duplicates
- Open the page source and confirm there is one canonical tag.
- Confirm the canonical points to the correct indexable URL.
- Check for parameter duplicates and alternate URLs.
If Google selects a different canonical, Google may index a URL that has little content, while ignoring the stronger version.
Step 7: Check JavaScript rendering and content delivery
- View the raw HTML from the server (not the rendered DOM).
- Confirm the main content exists in the HTML or loads reliably during render.
- Check if content requires blocked third-party scripts or cookies.
If you use a JS framework, Google can still render it, but failures happen with blocked resources, long tasks, and delayed API calls.
Step 8: Check internal links and sitemap signals
- Confirm the URL appears in your XML sitemap only if it is a real indexable page.
- Confirm the page has internal links from relevant pages.
- Remove orphan URLs from sitemaps unless they should rank.
Weak internal linking can push Google to index the URL but treat it as low value. The result can be “indexed without content” or poor ranking.
Next, you will map each root cause to a clear fix.
Common Causes (and What Each One Looks Like in GSC)
Use this section as a quick match. You can often identify the cause by what the rendered screenshot and HTML show in URL Inspection.
Cause 1: Soft 404 or empty state pages
A soft 404 happens when a page returns 200 but shows “not found,” “no results,” or near-empty content.
- GSC clue: Rendered screenshot shows a thin page, “no results,” or a blank content area.
- Site clue: Many URLs from internal search, filters, tags, or expired products.
Cause 2: Blocked resources (CSS/JS) or blocked API calls
- GSC clue: Page resources show blocked or failing files.
- Site clue: Content appears only after JS loads, but JS fails for Googlebot.
Cause 3: JavaScript rendering fails or content loads too late
- GSC clue: HTML preview has little text. Rendered screenshot misses main content.
- Site clue: Content relies on client-side fetch with slow endpoints.
Cause 4: Wrong canonical or duplicate URL variants
- GSC clue: Google-selected canonical differs from your canonical.
- Site clue: Parameters, uppercase/lowercase duplicates, trailing slash variants.
Cause 5: Server issues, bot protection, or inconsistent responses
- GSC clue: Live test works, crawled version looks empty, or fetch fails sometimes.
- Site clue: WAF rules, rate limits, geo blocks, or heavy caching differences.
Cause 6: Thin content or boilerplate-only templates
- GSC clue: Page renders but has very little unique text.
- Site clue: Tag pages with one item, empty categories, auto-generated pages.
Next, you will fix the issue with a practical checklist.
How to Fix “Page Indexed Without Content” (Action Checklist)
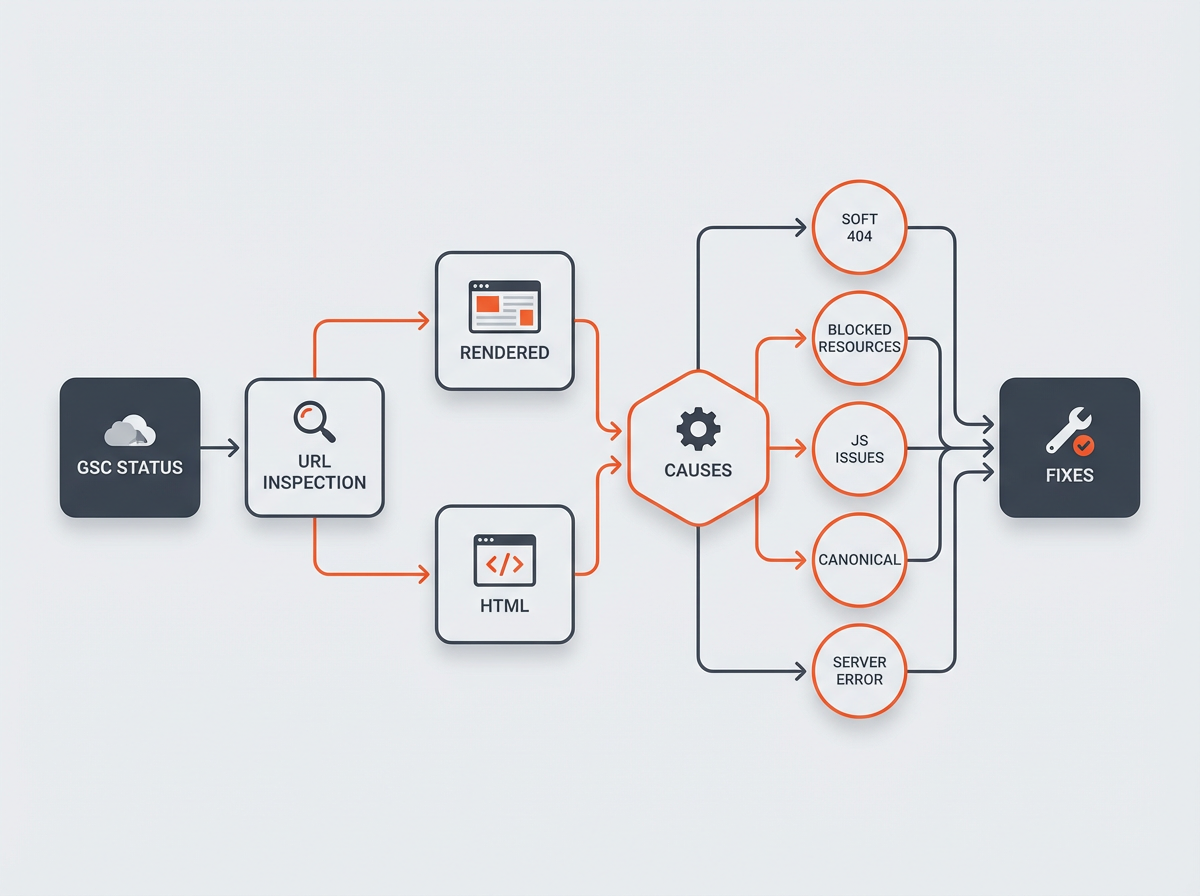
Apply the fix that matches your cause. Start with the highest-impact groups of URLs. Then re-test in URL Inspection.
Fix 1: Turn soft 404 and empty states into clear outcomes
- If a page should not exist, return 404 or 410.
- If a page should exist but has no items, add real content:
- Add a short intro that explains the page topic.
- Add links to related categories or popular items.
- Add helpful filters only if they produce indexable pages.
- If internal search pages get indexed, block them from indexing:
- Add
noindexto search results pages. - Remove them from sitemaps.
- Stop linking to them from crawlable pages.
- Add
Fix 2: Unblock critical resources needed for rendering
- Allow Googlebot to fetch CSS and JS files that build the layout and content.
- Check
robots.txtfor rules likeDisallow: /assets/,Disallow: /js/, or blocked API paths. - Confirm your CDN does not block Googlebot.
If you must block some resources, do not block the ones that load the main content.
Fix 3: Make content visible in the initial HTML (or use SSR)
- Render key content on the server (SSR) for important pages.
- Use static rendering for pages that must rank and do not change often.
- Reduce dependency on delayed API calls for above-the-fold content.
- Ensure the main content loads without user interaction.
This fix often removes “indexed without content” for JS-heavy sites.
Fix 4: Correct canonical tags and URL variants
- Set one preferred URL format (slash, lowercase, parameters).
- Use 301 redirects from non-preferred variants to the preferred URL.
- Set the canonical to the preferred URL and keep it consistent.
- For faceted navigation, decide which filter pages should be indexable:
- Index only pages with stable demand and unique content.
- Use
noindexfor low-value filter combinations.
Fix 5: Stop indexing low-value auto-generated pages
- Remove thin tag pages from sitemaps.
- Add
noindexto pages with no unique value. - Consolidate similar pages into one stronger page.
This reduces index bloat and improves crawl focus.
Fix 6: Fix server instability and bot blocking
- Check server logs for Googlebot requests and response codes.
- Allowlist Googlebot if your WAF blocks it by default.
- Reduce time to first byte (TTFB) and total load time.
- Fix 5xx errors, timeout errors, and redirect chains.
Fix 7: Googlebot Blocking in Cloudflare (Firewall, Bot Management, WAF Rules)
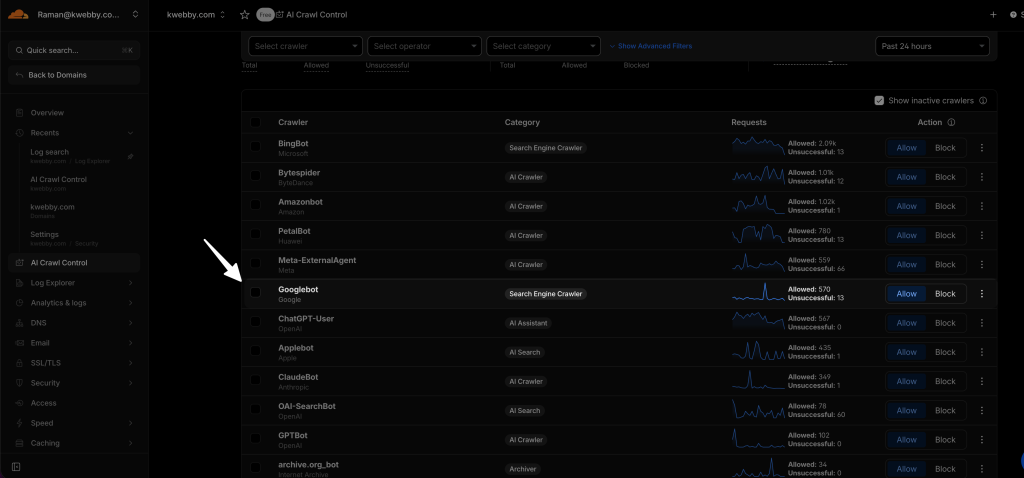
- Check bot settings of your property inside cloudflare
- Under AI Crawl Control make sure you have enabled “GoogleBot”
- Check detailed guide here: How to Fix Cloudflare Blocking Googlebot: Firewall, WAF, Bots
Next, you will validate your fixes and push Google to reprocess the URLs.
How to Confirm the Fix and Get Google to Reprocess Pages
Fixes do not help until Google recrawls and re-evaluates the page. Use these steps to confirm progress.
Step 1: Re-test with URL Inspection
- Run Test Live URL.
- Confirm the rendered screenshot shows the main content.
- Confirm the HTML preview includes meaningful text.
- Confirm the canonical is correct.
Step 2: Request indexing for key URLs
- In URL Inspection, click Request Indexing for your most important pages.
- Do this for a small set first. Confirm results. Then expand.
Step 3: Use “Validate Fix” in the Pages report
- Return to the Page indexing report.
- Open the issue group.
- Click Validate Fix after you deploy changes.
Step 4: Update sitemaps and internal links
- Submit an updated XML sitemap with only indexable URLs.
- Add internal links to important pages from relevant hubs.
- Remove internal links to low-value URLs you set to
noindexor 404.
Next, use these quick checks to answer the common indexing questions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I check if my page is indexed or not?
Use URL Inspection in Search Console and check if it says the URL is on Google. You can also search Google with site:yourdomain.com your-page-slug as a quick check.
How to check if something is indexed?
Check the URL in URL Inspection and review the Indexing section. For a second signal, use the site: operator and confirm Google shows the exact URL you expect.
How to fix page indexing issues?
Start in the Page indexing report, inspect sample URLs, then fix the root cause. Common fixes include removing noindex, correcting canonicals, unblocking resources, improving thin pages, and fixing server errors.
How to fix “Discovered – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console?
Improve internal links, include the page in a clean sitemap, and ensure the page returns fast 200 responses with real content. Remove low-value URLs and reduce duplicate variants so Google can prioritize the right pages.
Why does Google index a page but show no content?
Google may see an empty template, blocked resources, a rendering failure, or a soft 404. URL Inspection helps you confirm if Google fetched content in HTML and in the rendered view.
Should I use noindex or 404 for empty pages?
Use 404/410 when the page should not exist. Use noindex when the page can exist for users but should not appear in search (like internal search results or low-value filters).
Final Thoughts
“Page indexed without content” usually has a clear cause that you can confirm in Search Console with URL Inspection, rendered screenshots, HTML checks, and canonical review. Fix the root issue first, then validate with live tests, cleaner sitemaps, and stronger internal links. If you want faster results, start with the URL groups that matter most for traffic, apply the matching fix, and use Request Indexing for your top pages.
Call to action: Open Search Console now, export the affected URLs, inspect five samples, and apply one fix today. Your next crawl can turn empty index entries into pages that rank.